Behind the global trillion-token interaction: Open-source models shift from "one dominant player" to "a multitude of contenders," with China’s AI entering the top tier

OpenRouter platform's trillion-token data shows that the open-source model market share has risen to 33%, breaking the closed-source monopoly. China's open-source AI has achieved a historic breakthrough, with market share soaring from 1.2% to nearly 30% peak, with Qwen, DeepSeek, and others entering the global first tier. The market landscape has shifted from "one dominant player" to a multi-strong co-governance, with medium models (15B-70B) becoming mainstream, and agent reasoning surpassing text generation, with programming applications accounting for over 50%
Based on empirical research from the OpenRouter platform, which covers over 100 trillion tokens, the large language model market is undergoing profound restructuring. The share of open-source models has risen to 33%, completely breaking the monopoly of closed-source models. The market landscape has shifted from DeepSeek's "dominance" to diversified competition, with Chinese open-source AI emerging strongly in this transformation, officially entering the global first tier.
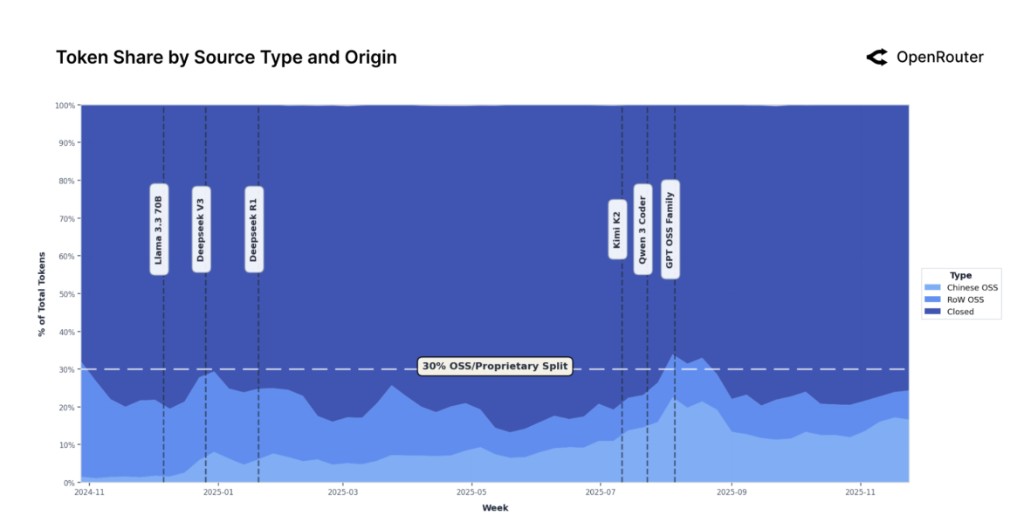
On December 4th, Silicon Valley's renowned venture capital firm a16z and the large model API platform OpenRouter stated in a jointly written report that the core driving force behind this transformation comes from the explosive growth of Chinese models. Data shows that the market share of open-source models developed in China skyrocketed from 1.2% at the end of 2024 to nearly 30% by mid-2025, with an average annual share of 13.0%, almost on par with the 13.7% share of open-source models in other parts of the world. Chinese models such as Qwen, DeepSeek, and MoonshotAI have made the leap from marginal participants to core players due to their technological capabilities and localization advantages.
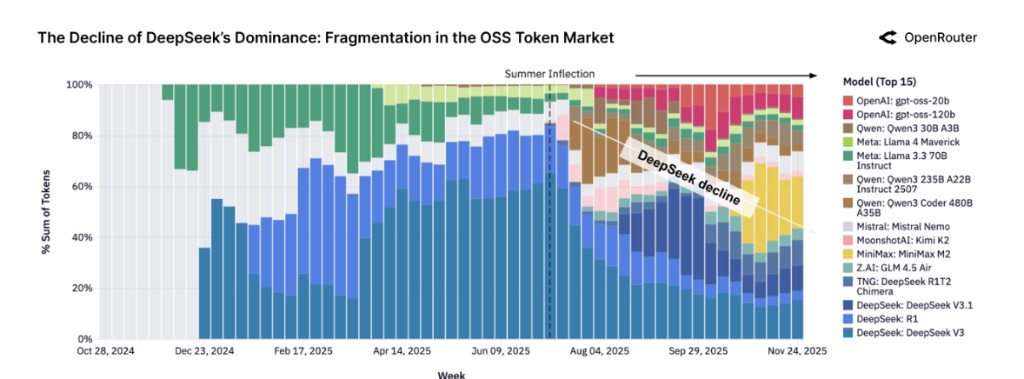
The report points out that the competitive landscape within the open-source ecosystem is undergoing a simultaneous transformation. After the "summer inflection point" in mid-2025, the market quickly shifted from a highly concentrated state where the DeepSeek family held over 50% of the share to fragmented competition. By the end of 2025, no single model will be able to maintain over 25% market share, and the user selection logic will shift from locking in the "best model" to flexibly combining 5-7 top models.
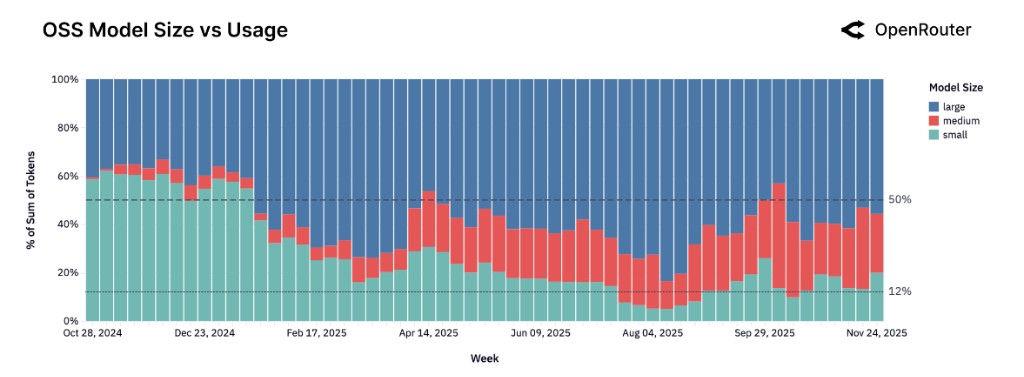
In addition, the research report reveals several disruptive trends: medium-sized models (15B-70B) are replacing small models as the mainstream, agent reasoning capabilities are surpassing text generation as the core value, the share of programming applications has surged from 11% to over 50%, and the spending share in the Asian market has doubled from 13% to 31%. The competitive rules have shifted from leaderboard scoring to real-world usage retention and workload matching capabilities.
Chinese Power Reshaping the Open-Source Landscape
The report states that the open-source model market has formed a dual-track structure of "closed-source defining performance limits, open-source providing diverse value." By the end of 2025, the market share of open-source models is steadily climbing to 33%. This growth is not a short-term trend but is driven by the continuous iteration of high-quality models such as DeepSeek V3 and Kimi K2.
The rise of Chinese open-source models has exceeded expectations. At the end of 2024, the market share of Chinese models was only 1.2%, but by mid-2025, its peak had reached nearly 30%. Chinese models such as Qwen, DeepSeek, and MoonshotAI have demonstrated unique advantages in technological capabilities and localization, marking China's official entry into the global first tier of the open-source race.
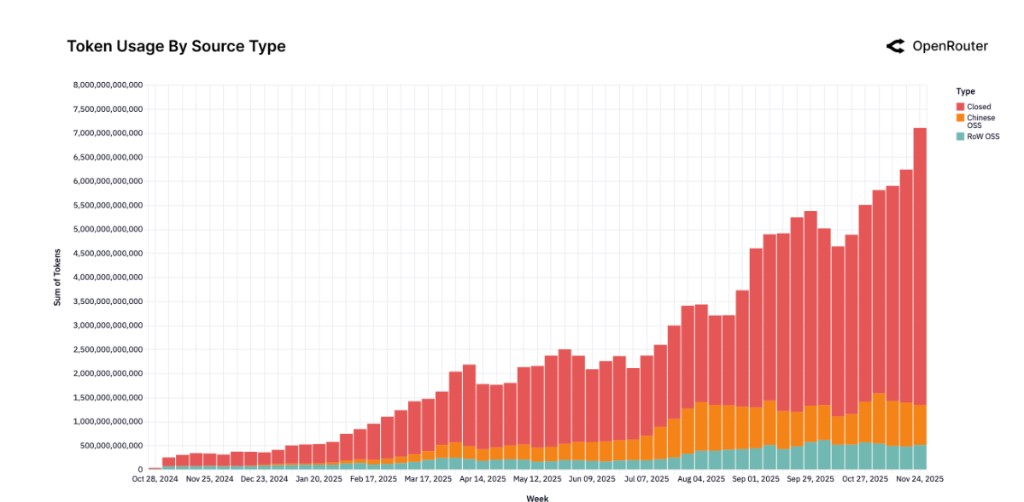
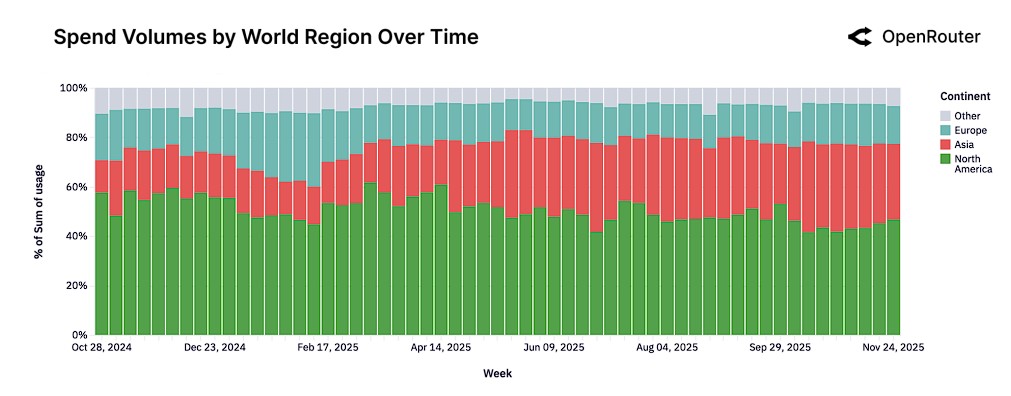
From a global regional distribution perspective, the overall rise of the Asian market is the most significant, with its share of global spending doubling from 13% at the beginning of the study to 31%, becoming a key growth engine. North America, while still the largest single region, has had its spending share remain below 50% for a long time.
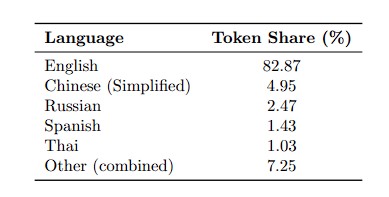
Language distribution data shows that Simplified Chinese accounts for 4.95%, making it the second largest language after English, reflecting strong demand from the Chinese market.
From Monopoly to Multi-Strong Co-Governance
According to the report, the open-source market at the end of 2024 presents a highly concentrated pattern, with the DeepSeek family’s V3 and R1 models collectively occupying over 50% of Token usage, almost forming a "monopoly" situation. However, this pattern is completely overturned after the "summer turning point" in mid-2025.
With the intensive release of new models such as Qwen, Minimax, Kimi K2, and the GPT-OSS series, the competitive barriers in the open-source market have been broken. These new models achieved large-scale production-level applications within weeks of their release. By the end of 2025, no single model can maintain over 25% of the open-source market share.
User behavior patterns have undergone fundamental changes. Developers have shifted from defaulting to "the best model" to diversifying combinations among 5-7 top models. This change marks the formal entry of the open-source ecosystem into a fully competitive stage of "warlord division," where a multi-model ecosystem becomes the industry norm.
"Medium is the New Small" Disrupts Size Perception
Empirical data of over one hundred trillion Tokens has completely overturned the traditional perception that "the open-source ecosystem is dominated by small lightweight models." Data shows that developers are reshaping the model size landscape through their actions.
Small models (<15B) continue to increase in number, but their total usage share is continuously shrinking, and the market is highly fragmented, making it difficult to form stable usage stickiness.
In contrast, medium models (15B-70B) have experienced explosive growth from non-existence, with medium models represented by Qwen2.5 Coder 32B rapidly building a fiercely competitive ecosystem.
These models precisely match users' needs for a "balance point between capability and efficiency," becoming the core growth pole of the open-source market, confirming the industry’s new consensus that "medium is the new small."
The large model (>70B) sector also shows a diversified competitive landscape, with models like Qwen3 235B and Z.AI GLM 4.5 becoming core benchmarks, as users tend to switch flexibly among multiple top large models
The Chinese Characteristics of Application Scenarios
From the overall task distribution of open-source models, role-playing has become the largest application with over 50% token share, benefiting from the inherent advantages of fewer content restrictions in open-source models. Programming assistance ranks second with a 15%-20% share, and its share continues to grow.
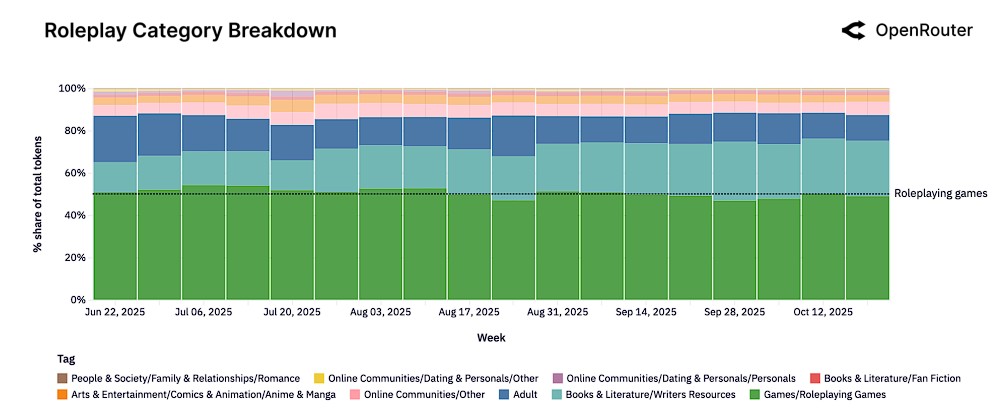
However, Chinese open-source models exhibit significant differentiated characteristics. Unlike the global market where "role-playing dominates," the combined share of programming and technical applications in Chinese open-source models reaches 39%, exceeding the 33% share of role-playing.
This difference indicates that Chinese open-source models have the capability to directly compete with world-class models in productivity areas such as code generation and technical reasoning. Their value proposition leans more towards enhancing professional efficiency rather than entertainment interaction, which may create a unique competitive advantage for Chinese models in the enterprise market.
Intelligent Agent Reasoning Leads Paradigm Shift
The most disruptive finding revealed by the research is the fundamental paradigm shift in the use of LLMs—from single-turn text completion to multi-step, tool-integrated intelligent agent reasoning workflows.
The volume of tokens processed by models optimized for reasoning has surged from nearly negligible levels at the beginning of 2025 to over 50% of total usage. This change is driven by both supply and demand:
On the supply side, the release of models like GPT-5 and Claude 4.5 has significantly raised the upper limit of reasoning capabilities; on the demand side, users increasingly prefer models that can manage task states, follow multi-step logic, and support intelligent agent workflows.
Accompanying the rise of intelligent agent reasoning are two key features:
The length of prompts has dramatically increased, with the average number of input tokens per request growing nearly fourfold from 1.5K to over 6K, where programming task prompts exceed 20K, which is 3-4 times that of other categories;
Tool invocation is becoming increasingly common, with models like Claude 4.5 Sonnet and Grok Code Fast leading the way, marking a fundamental shift of LLMs from "text generators" to "action executors."
"Cinderella's Glass Slipper Effect" Defines New Moat
The research has identified a group of "foundational user groups" with exceptionally high long-term retention and proposed the "Cinderella's Glass Slipper Effect" framework to explain this phenomenon, defining the core moat of the AI era.
The core logic of this framework is: There always exists a high-value "workload" in the market that remains unmet; each generation of new model releases is a "trying on the glass slipper" matching process; when a model perfectly addresses the technical and economic constraints of a specific workload for the first time, users will build processes and data pipelines around that model, creating extremely high switching costs and stickiness Data confirms this logic: The early foundational user retention rate for Claude 4 Sonnet and Gemini 2.5 Pro remains at 40% after five months, while models like Llama 4 Maverick, which failed to achieve matching, show poor retention across all user groups. Additionally, the DeepSeek model exhibits a unique "boomerang effect," where some churned users return after trying other models.
This finding reveals that the true competitive barrier comes from the initial matching of "workload-model" and the resulting high stickiness of the foundational user group, with retention being far more critical than growth. The industry's focus is shifting from slight advantages in rankings to empirical analysis and operational optimization in real-world usage, moving from single model competition to flexible multi-model strategies, with open-source and closed-source, East and West coexisting and competing in the long term