OTC Trading/Pink Sheets FAQs
Here you'll find quick answers to common questions about over the counter trading.
1. What is over-the-counter (OTC) trading?
Over-the-counter (OTC) trading, also known as off-exchange trading, occurs in the OTC market. Unlike traditional exchanges, the OTC market does not have a physical location or a set group of members and is not regulated by a securities exchange. Instead, trades are conducted through a network of brokers, and the prices are not always publicly disclosed.
The OTC market includes approximately 10,000 different types of securities, such as large American Depositary Receipts (ADRs), foreign ordinary shares, and stocks of small and micro-cap growth companies. Some OTC securities report to the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), while others may follow different reporting standards or not report at all.
2. Pros and Cons of OTC Trading
Securities listed on regulated exchanges must adhere to stringent listing requirements, and issuers must fulfill comprehensive disclosure obligations. These regulations can impose significant costs on smaller or startup companies. Non-listed securities are not inherently inferior; they simply may not have applied for exchange listing due to various strategic reasons. In the U.S., for instance, newly issued federal securities, municipal bonds, and corporate bonds can all be traded OTC.
(Please note: Investing in OTC securities carries higher risks compared to on-exchange trading. Investors should understand the risks and background of the securities before investing.)
Pros
- Market facilitation: Smaller or startup companies might face challenges on regulated exchanges due to low liquidity of their securities. Intermediaries in the OTC market help facilitate trades, supporting the growth of emerging markets.
- Large trades in the OTC market can fulfill the needs of both buyers and sellers while potentially reducing short-term price volatility in the public market.
- The OTC market is less regulated than exchanges, offering speculative investors the opportunity to pursue potentially higher returns.
Cons
- Less regulation can result in issues such as counterparty defaults, making OTC trading riskier than exchange trading.
- OTC products generally lack strict disclosure requirements, making it hard for investors to find company information, which can impact investment decisions.
- OTC products often lack liquidity, which means that they can be hard to buy or sell, or may result in unfavorable transaction prices.
3. OTC Market Tiers
OTC Markets Group employs a three-tiered system based on the quality and quantity of information disclosed about OTC products. This system does not indicate the stock's quality or risk but serves as a guide for investors to exercise caution before investing. The tiers are as follows:
OTCQX
OTCQX is the top tier of the three marketplaces. Companies in this tier must provide timely and comprehensive disclosure of regulatory information, maintain audited financial statements, and are not classified as penny stocks, shell companies, or bankrupt entities. Certain exceptions apply, such as certain foreign companies that issue American Depositary Receipts (ADRs) in the U.S., which may also fall under the OTCQX category.
OTCQB
The middle tier is called OTCQB, which consists of early-stage and developing companies. Companies in this tier must have a minimum bid price of USD 0.01 and provide up-to-date regulatory reports. They must also have their annual financials reviewed according to U.S. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and must not be in bankruptcy.
Pink Market
The Pink Market is an open market that imposes no minimum financial standards and encompasses a diverse range of companies, including foreign entities, penny stocks, shell companies, and others that opt not to disclose financial information. These companies often have smaller scales and uncertain growth prospects.
4. How do I view OTC stock?
To view OTC stocks, follow these steps in the Longbridge App: Navigate to "Market" -> Tap the magnifying glass icon -> Enter the OTC stock symbol
5. How do I know if a stock is traded OTC?
To check if a stock is traded OTC, follow these steps in the Longbridge App: Navigate to the Stock details page -> Tap the stock symbol icon in the upper right corner
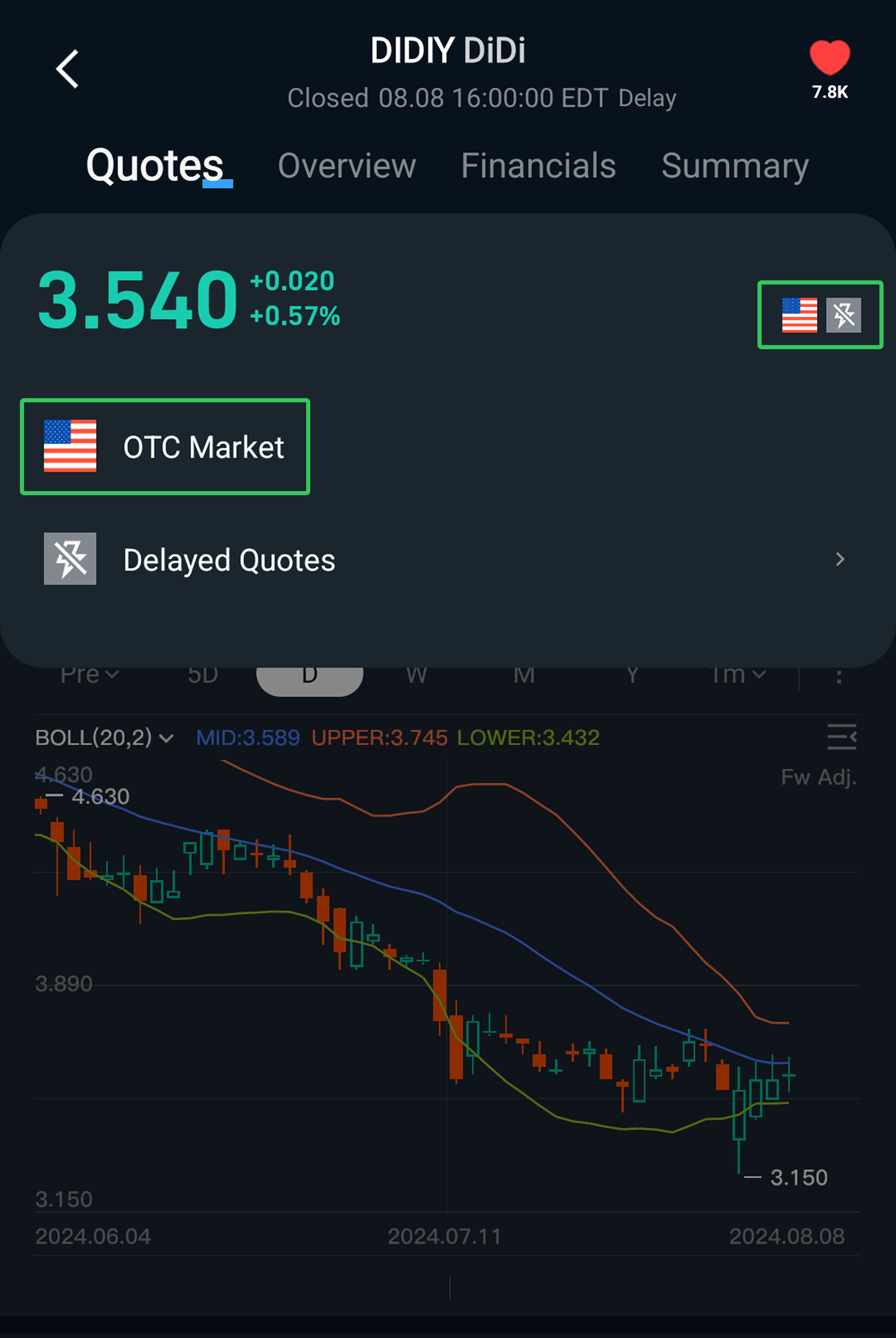
6. Does Longbridge support trading OTC stocks?
Yes, Longbridge supports trading of some OTC stocks.
7. Do OTC stocks support pre/post-market trading?
OTC stocks are only available for trading during regular trading hours for the U.S. market.
8. Why was my OTC / pink sheet limit order not submitted to the market?
Your order may not have met the minimum trading quantity requirements. Please ensure that your limit order aligns with the minimum trading quantities outlined below. If your order cannot be submitted or executed, you will receive a rejection message.
Minimum trading quantity requirements for OTC stocks:
| Price (Bid or Ask) | Minimum Trading Quantity |
| 0.0001–0.0999 | 10,000 shares |
| 0.10-0.1999 | 5,000 shares |
| 0.20–0.5099 | 2,500 shares |
| 0.51–0.9999 | 1,000 shares |
| 1.00–174.99 | 100 shares |
| 175.00 | 1 share or more |
Disclosures
This article is for reference only and does not constitute any investment advice.

