
 Posts
Posts Likes Received
Likes ReceivedJ&T: Can the "Pinduoduo" of the express delivery industry continue to sprint?

For investors familiar with J&T, there are many similarities between J&T Express and the booming domestic e-commerce platform Pinduoduo. First of all, both companies' founders have been influenced by Duan Yongping. In terms of corporate culture, they both adhere to a rough management philosophy of "just enough" and prioritize big issues over small details. In terms of development strategy, they both focus on providing the best cost-effectiveness and initially achieved rapid business growth through substantial investments. They have also achieved impressive performance growth, with J&T becoming the sixth largest express delivery player in China within just over two years, with a daily average of over 30 million parcels.
So, the question we hope to answer in this article is: how did J&T become a leading player in the highly competitive and oversupplied domestic express delivery market in just two years? Besides burning money on subsidies, what is J&T's core advantage? And how did J&T become the industry leader in Southeast Asia (using a similar approach as in China)? Finally, in terms of investment opportunities, can J&T, with similar genes to Pinduoduo, defy the weak market environment and deliver substantial returns to investors?
In summary, Dolphin Research's conclusion is as follows: 1) In the slowing growth and increasingly competitive domestic express delivery market, J&T initially relied on extreme low prices and support from Pinduoduo to quickly become the sixth largest player in the industry. However, there is still a certain gap between J&T and the top players in terms of operational efficiency and cost reduction, which cannot be sustained by competing solely on low prices. The period of gaining market share through loss-making and low-price competition has come to an end for J&T. The next few years will be a phase for J&T to improve its operational efficiency and turn profits.
As for the Southeast Asian market, J&T, with its leading operational approach in the domestic express delivery industry, has disrupted the inefficient, expensive, and slow local express delivery companies with a "SF Express" style of high efficiency, good service, and strong management. This demonstrates that although the market conditions in the two regions are different, the rule of "efficiency wins the market" remains the same. It also proves that J&T's "barbaric growth" approach in China is not a long-term strategy.
In terms of valuation, according to our calculations, J&T's current issue price of HKD 12 already reflects the company's foreseeable and deliverable performance, making it less cost-effective. From a long-term perspective, J&T has not yet formed a real competitive advantage in China. The future growth potential mainly lies in Southeast Asia and cross-border markets. Currently, Dolphin Research does not see any long-term holding opportunities.
However, the public offering of shares this time only accounts for about 3% of the total shares, so there may be significant fluctuations in the stock price in the early stages of listing. But for such short-term investment opportunities, Dolphin Research can only advise investors to exercise caution.
First, let's clarify the question that serves as the introduction to the subsequent analysis: what kind of logistics company is J&T? In summary, J&T, founded in 2015, started its express delivery business in Southeast Asia with the advanced experience of the domestic express delivery industry.And after becoming a leading player in Southeast Asia, in 2019, J&T began to expand its domestic express delivery business through "export-to-domestic sales". As of 2022, J&T is currently the largest express delivery company in terms of volume in Southeast Asia and the sixth largest in China.
J&T focuses on scale in China and profitability overseas. According to the company's financial data, revenue from domestic operations increased nearly tenfold to over $40 million from 2020 to 2022 (including the contribution from Best Express). During the same period, although Southeast Asian e-commerce also benefited from the pandemic and experienced robust growth, its revenue only increased by about double to $24 million. In terms of revenue structure, in 2020, J&T's revenue was 70% from Southeast Asia and 30% from China. However, by 2022, it had changed to nearly 60% from China, 30% from Southeast Asia, and about 10% from cross-border and overseas markets. This shows that although J&T's domestic business started later, it has become the main source of revenue.
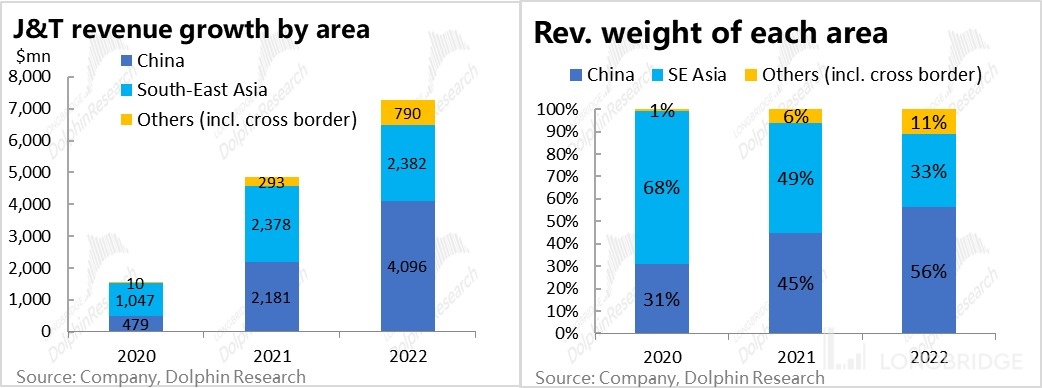
However, in terms of profit contribution, as of 2020, only the Southeast Asian region, the "home base," achieved stable profitability, while China and new markets continued to incur losses (although domestic losses have been narrowing). In summary, although J&T's growth momentum in the Chinese market is impressive, it is more about building scale and reputation, while the Southeast Asian market is where J&T truly generates profits and holds market position.
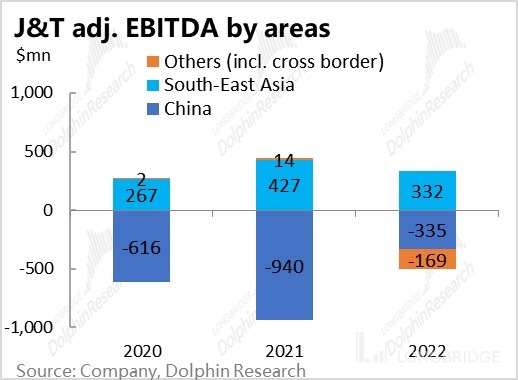
Therefore, Dolphin Research believes that when evaluating J&T's valuation in the future, the Southeast Asian business should be considered as the cornerstone, while the Chinese and overseas businesses represent the upward potential and room for imagination. The following analysis of J&T will focus on the two major segments: domestic and Southeast Asian markets.
Second, with sluggish growth and intensified competition, the domestic express delivery market is a "tough business."
Let's first look at the more familiar domestic market. The first question is, what kind of market did J&T enter after three years of effort and billions of losses in the domestic express delivery industry? What will be the return on J&T's investment?
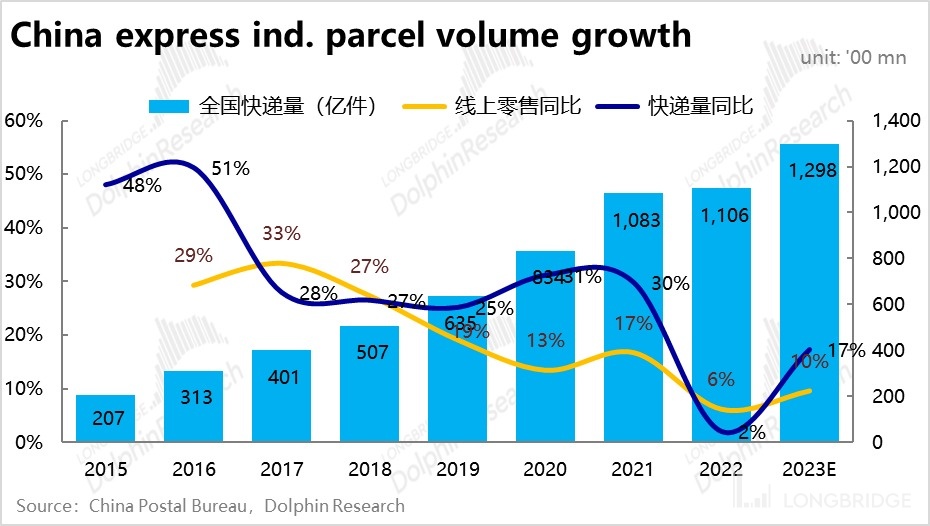
In general, the development of the domestic express delivery industry is closely tied to the rise and fall of the e-commerce industry. It is estimated that in 2022, out of the total of over 100 billion express parcels in China, about 90% are related to e-commerce. It can be said that the domestic express delivery industry mainly serves the fulfillment needs of e-commerce. Therefore, the demand for express delivery is generally consistent with the growth trend of online retail sales.
Since 2015, as the online retail penetration rate in China gradually approaches saturation and the growth rate slows down, the growth rate of express delivery volume has also declined from around 50% in 2015 to around 10%+.Looking ahead, the growth of the domestic e-commerce industry is likely to slow down steadily. Even though there is a trend of decreasing value per package in online shopping, the growth of package volume in express delivery will be slightly higher than the overall growth rate of the e-commerce market. However, it is also highly likely that the growth will continue to slow down.
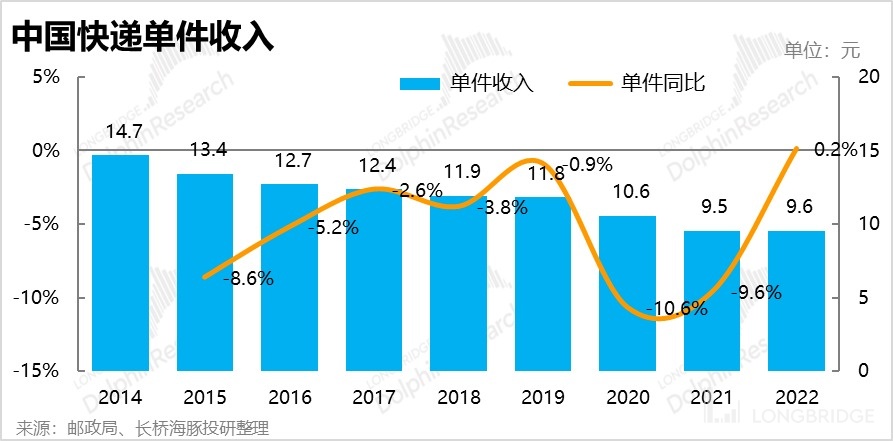
In addition to the limited overall growth rate of the industry, another significant pain point in the express delivery industry is the oversupply of transportation capacity, which has led to intense competition within the industry. As shown in the graph below, the average price of express delivery in China has been declining since 2014, from a peak of 14.7 yuan per package to only 9.6 yuan in 2022, a decrease of nearly 35%. The downward trend in the average price of express delivery can be attributed to the economies of scale brought about by the industry's expansion and the efficiency improvements resulting from management and technological advancements. However, the oversupply and intense competition in the domestic express delivery market are the key reasons for the continuous decline in unit price.
In comparison with other markets, the three major express delivery operators in the United States accounted for nearly 80% of the market share in 2020. If we add the market share of the e-commerce platform Amazon (which is said to have surpassed FedEx), the entire U.S. express delivery market is basically monopolized by four major players.
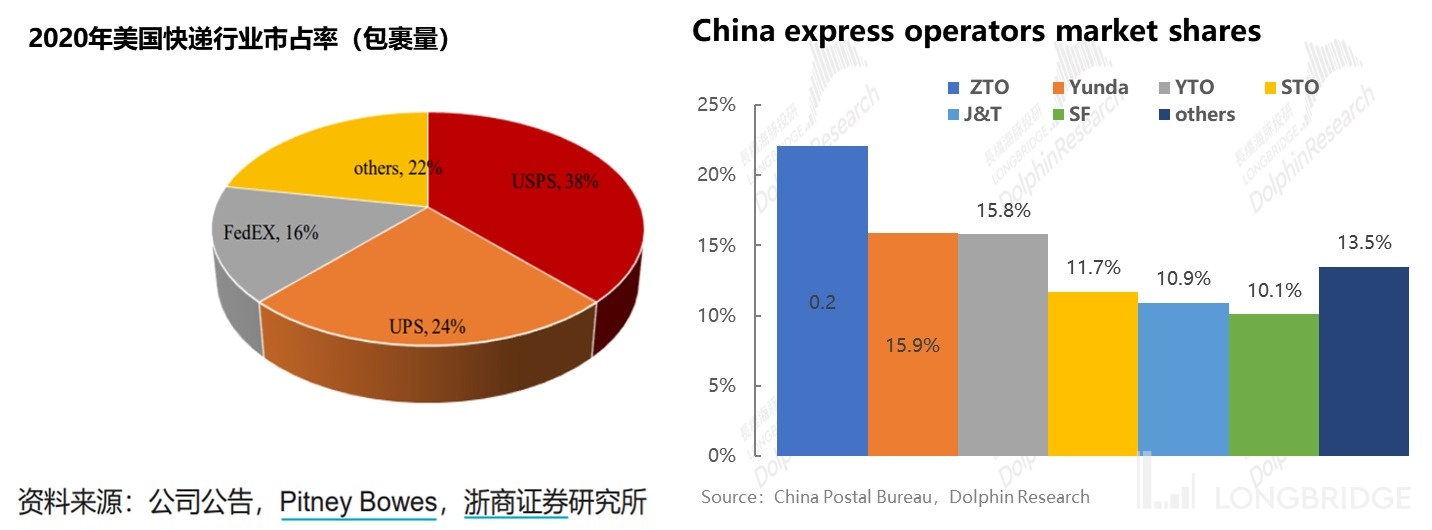
In contrast, the top express delivery companies in China include SF Express, YTO Express, ZTO Express, JD Logistics, and China Post EMS, totaling eight major players. Except for China Post, the market share of each express delivery company is concentrated between 20% and 10%. It can be seen that the market share in the domestic express delivery industry is more dispersed, and there is no significant gap between the top players, leading to a competition pattern where no one is willing to yield to others. Therefore, the path of industry consolidation, which is a direct and effective way to eliminate excess capacity, is difficult to achieve.
The intense competition within the industry is the fundamental reason for the decline in unit price, which has also resulted in a continuous decrease in gross profit per package despite the continuous growth in package volume for each express delivery company in recent years, indicating an uneconomical scale.
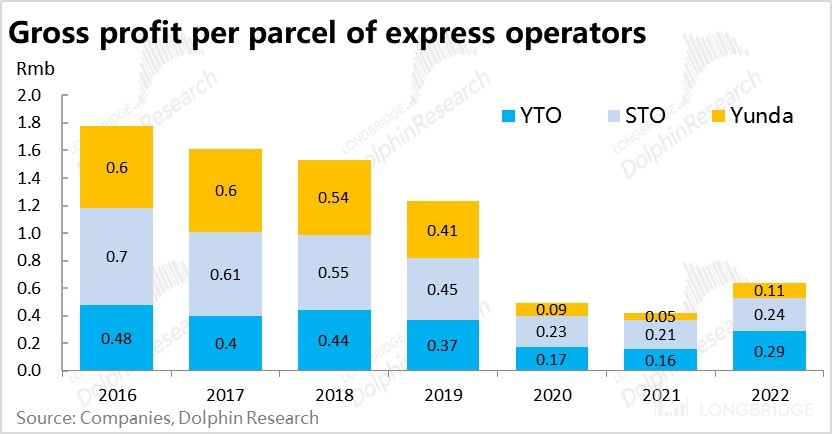
In summary, the domestic express delivery industry is currently in a cycle of slowing growth, intense competition, and increasing revenue but not profitability, which is clearly not a good business. Moreover, the "price war" initiated by ZTO Express upon entering the domestic market directly led to a significant decline in the average gross profit per package for domestic express delivery companies in 2020-2021, which only rebounded in 2022. It can even be said that entering the domestic express delivery industry under such circumstances is a lose-lose situation, harming others and oneself.
Is J&T competitive in China?
1. Conclusion: J&T is "superficially" impressive, but there is still room for improvement in its "internal strength".
From an industry perspective, the domestic express delivery market is not necessarily a lucrative business. So, in this highly competitive industry, how has J&T performed and what are its "core" competitive advantages? Let's start with its achievements:
In terms of parcel volume, J&T exceeded 12 billion parcels in 2022, with a market share of 10.9%, ranking 6th in the domestic market.
In terms of fixed assets, looking at the number of sorting centers, trunk vehicles, and end stores, J&T is on par with other leading players, without any significant advantages or weaknesses.
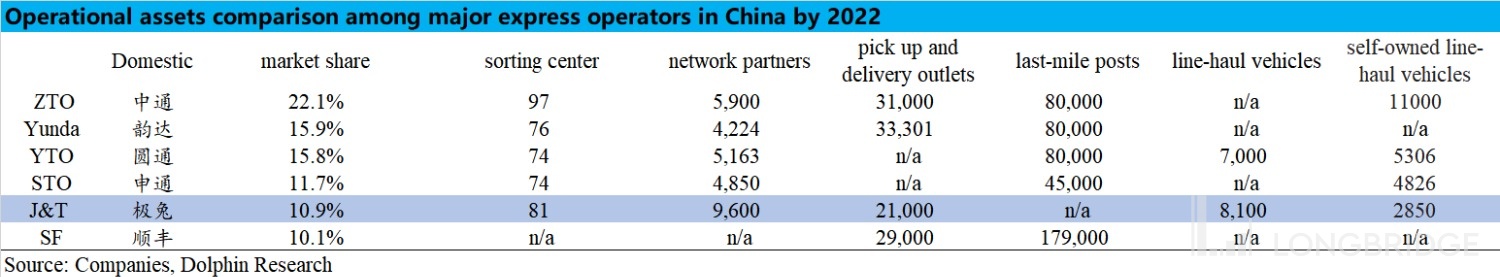
Therefore, in terms of the "surface" business scale, J&T has caught up with the industry leaders within three years. However, in terms of "internal strength" in terms of operational efficiency and profitability:
③ In terms of average revenue per parcel, it was only $0.23 in 2020, which is 1/3 lower than the other three major players (indicating that J&T relies on extremely low prices to gain market share). However, in the following two years, as J&T's parcel volume increased and the government implemented policies to prohibit vicious price wars in the express delivery industry, by 2022, J&T's average revenue per parcel had increased to $0.34, only slightly lower than the other three major players by $0.02-$0.04, maintaining a reasonable level of cost-effectiveness.
④ In terms of average cost per parcel, from 2020 to 2022, although J&T's average cost per parcel decreased from $0.5 to $0.4, it is still $0.05-$0.07 higher than its counterparts.
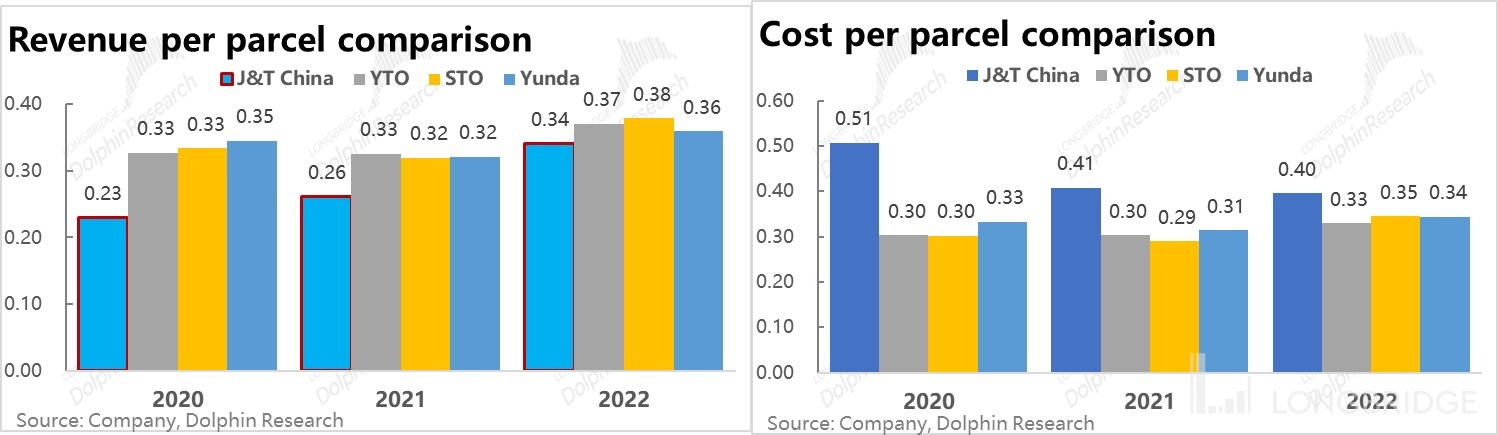
While the average revenue per parcel is lower by 2-3 cents, the average cost is higher by 5-7 cents, resulting in J&T still incurring a loss of approximately 6 cents per parcel in 2022. In comparison, Yunda Express, which has the thinnest profit margin in the industry, has a gross profit of 2 cents per parcel. It can be seen that J&T still has a significant gap in operational efficiency and cost control in terms of "internal strength".
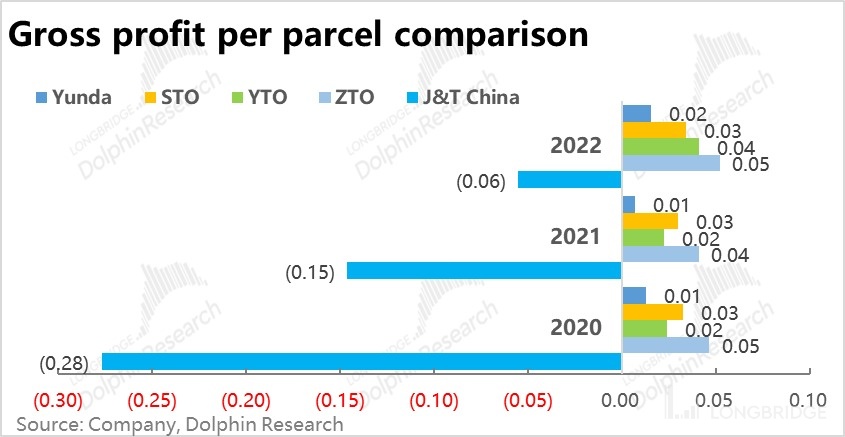
2. Causes: Where does J&T fall short?From the perspective of results, it can be seen that although J&T's growth rate is impressive and on par with the industry leaders, there is still a gap in terms of internal management and operational efficiency. So, from a business perspective, what are the characteristics and strategies of J&T's company?
Dolphin Research believes that the fundamental reason for J&T's rapid growth but continued losses in the domestic market can be attributed to the following points:
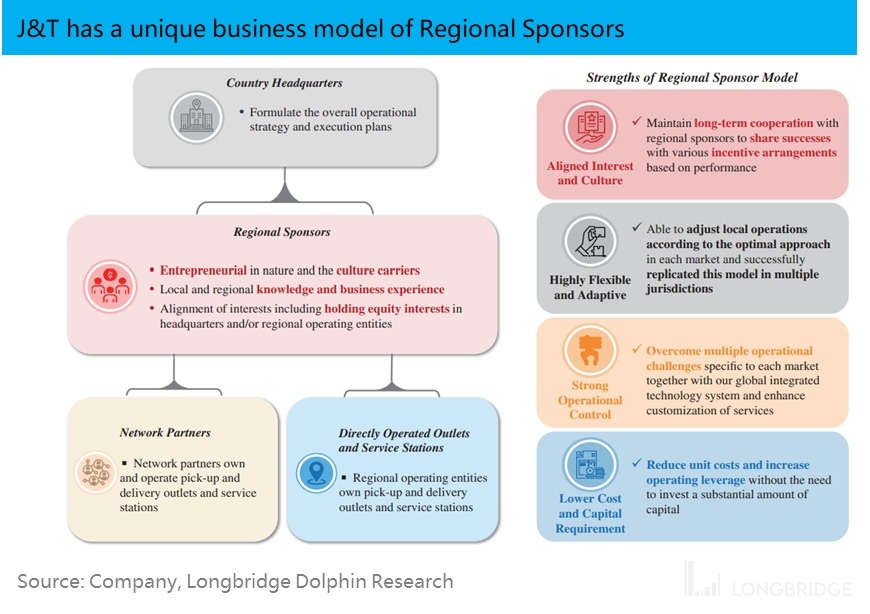
Unique three-tier franchise model conducive to rapid expansion: Unlike the common two-tier franchise system (headquarters and franchisees) adopted by domestic industry leaders such as Shunfeng, J&T employs a unique three-tier franchise system consisting of the national headquarters, regional partners, and terminal franchise stores. The main difference is that J&T has an additional layer of regional partners.
Under the traditional franchise model, express delivery companies are responsible for investing in and operating nationwide transfer and sorting centers, trunk transportation, and back-end management. They recruit franchisees to handle customer acquisition, order collection, and delivery, thereby forming a complete distribution network.
In J&T's model, J&T establishes a cooperative relationship with regional partners, and the operation and recruitment of terminal outlets within the region are mainly handled by the regional partners. The regional partners also participate in and share the construction of transfer centers and trunk transportation.
This means that J&T has delegated a significant portion of the management pressure on terminal outlets and the financial burden of building a logistics network to regional franchisees. Therefore, J&T's business model naturally adapts to rapid expansion, similar to the "land grab" strategy.
Scale precedes efficiency: However, as the other side of the coin, the unique regional partner system not only brings flexibility for expansion but also naturally leads to weaker control over terminal outlets and some non-self-operated sorting centers, resulting in lower management efficiency.
In the competition within the express delivery industry, the ultimate goal is to maximize the efficient utilization of transportation capacity and manpower to achieve the lowest average cost per order. This allows companies to obtain the highest profit under the same pricing or provide the lowest pricing under the same profit, thereby achieving economies of scale and a positive cycle of profitability.
As a validation, ZTO Express, which has the highest market share in the Chinese express delivery industry, also has the highest average gross profit per order. Conversely, J&T and STO Express, which have the lowest average gross profit per order, also have the lowest market share among franchise-based express delivery companies. Therefore, for express delivery companies, achieving the highest efficiency is the key factor determining success or failure.
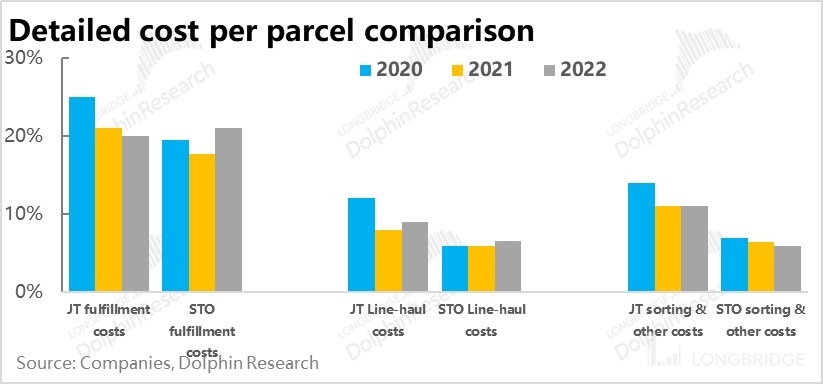
So, what are the main differences in efficiency between J&T and other players? As seen from the above chart, compared to STO Express, which has similar scale efficiency, J&T's actual cost for last-mile delivery is not significantly different from STO's. However, there is still a considerable gap between J&T and STO in terms of labor costs for trunk transportation and sorting centers, which reflect the efficiency of headquarters operations, as of 2022.Verification has shown that although J&T has experienced rapid growth in scale within three years, there is still a lot of work to be done in terms of operational efficiency and effectiveness.
③ Unsustainable Losses from Low Prices: Although J&T was able to rapidly expand its scale by offering prices about 1/3 lower than its competitors, the price war initiated by J&T in the Yiwu region in early 2021, which brought the price per item below 1 yuan, alarmed regulatory authorities. After the authorities intervened and prohibited express delivery pricing below cost, J&T was forced to raise its prices to a level close to that of Shentong and Yunda.
However, low prices without cost advantages cannot be sustained in the long term. Currently, the gap between J&T's average revenue per item and that of Shentong and Yunda has significantly narrowed. Moreover, with consecutive losses and the pressure to achieve profitability after going public, J&T must quickly turn a profit. Relying solely on the advantage of attracting customers through low prices is difficult to maintain in the long run. Once J&T gradually loses its absolute price advantage, it will be challenging for them to further capture market share if they cannot strengthen their operational efficiency.
④ Has the honeymoon between J&T and Pinduoduo ended? As mentioned earlier, e-commerce consumption is the main source of domestic express delivery demand, and J&T's entry into China at the end of 2019 coincided with the period when Pinduoduo experienced rapid growth, transforming from a player outside the fifth ring road to the third (possibly second) largest e-commerce platform in the country. According to media reports, 80%-90% of J&T's domestic order volume between 2020 and 2021 originated from the Pinduoduo platform. During the same period, Pinduoduo's total order volume increased from less than 20 billion in 2019 to nearly 70 billion in 2022, nearly 2.5 times growth.
It can be said that the combination of Taotian & Shentong and JD & JD Logistics had already formed a stable competition pattern in the e-commerce and logistics industry. It was Pinduoduo's rise and support that gave J&T the opportunity to break the existing pattern and emerge as a leading player in the already oversupplied express delivery track.
However, since 2021, Pinduoduo has gradually integrated SF Express, Shentong, and JD Logistics as the preferred express delivery providers for merchants. Based on Dolphin Research's observation when using Pinduoduo, the proportion of orders delivered by J&T is not high, and there is no significant difference compared to Shentong and Yunda. Large and valuable items such as home appliances are mostly delivered by JD or Shunfeng. After supporting J&T to achieve its initial volume, it seems that Pinduoduo is no longer giving special treatment to J&T.
Therefore, in terms of domestic operations, the honeymoon period of relying on the rapid growth of Pinduoduo and the initial volume has basically ended. In the future, the focus will inevitably return to the competition based on operational efficiency and cost control mentioned earlier.
III. Southeast Asia is J&T's "ballast stone"
1. How is the express delivery industry in Southeast Asia?
The domestic express delivery market is already a sunset industry to some extent, so what kind of market is Southeast Asia? According to Dolphin Research's previous study, "Is it better to stay in a corner or venture across the sea? Southeast Asia is still the 'land of dragon's prosperity' for SEA," the characteristics of the Southeast Asian region include: ① The total population of the region exceeds 600 million, with a higher proportion of young people and higher growth rates. The population is large enough and more dynamic.② The potential for future economic growth is high. According to the IMF's forecast in 2021, the compound annual growth rate of GDP between 2020 and 2025 is expected to reach 7.6%, significantly higher than other mature economies (although there has been a weakening trend in Southeast Asian economies since 2023, and the growth rate expectations should be adjusted downwards). ③ However, the total GDP and per capita income are still low. As of 2020, per capita income is less than $5,000, less than half of China's. In summary, the market space is large, the growth potential is good, but the infrastructure is weak and further development is needed.
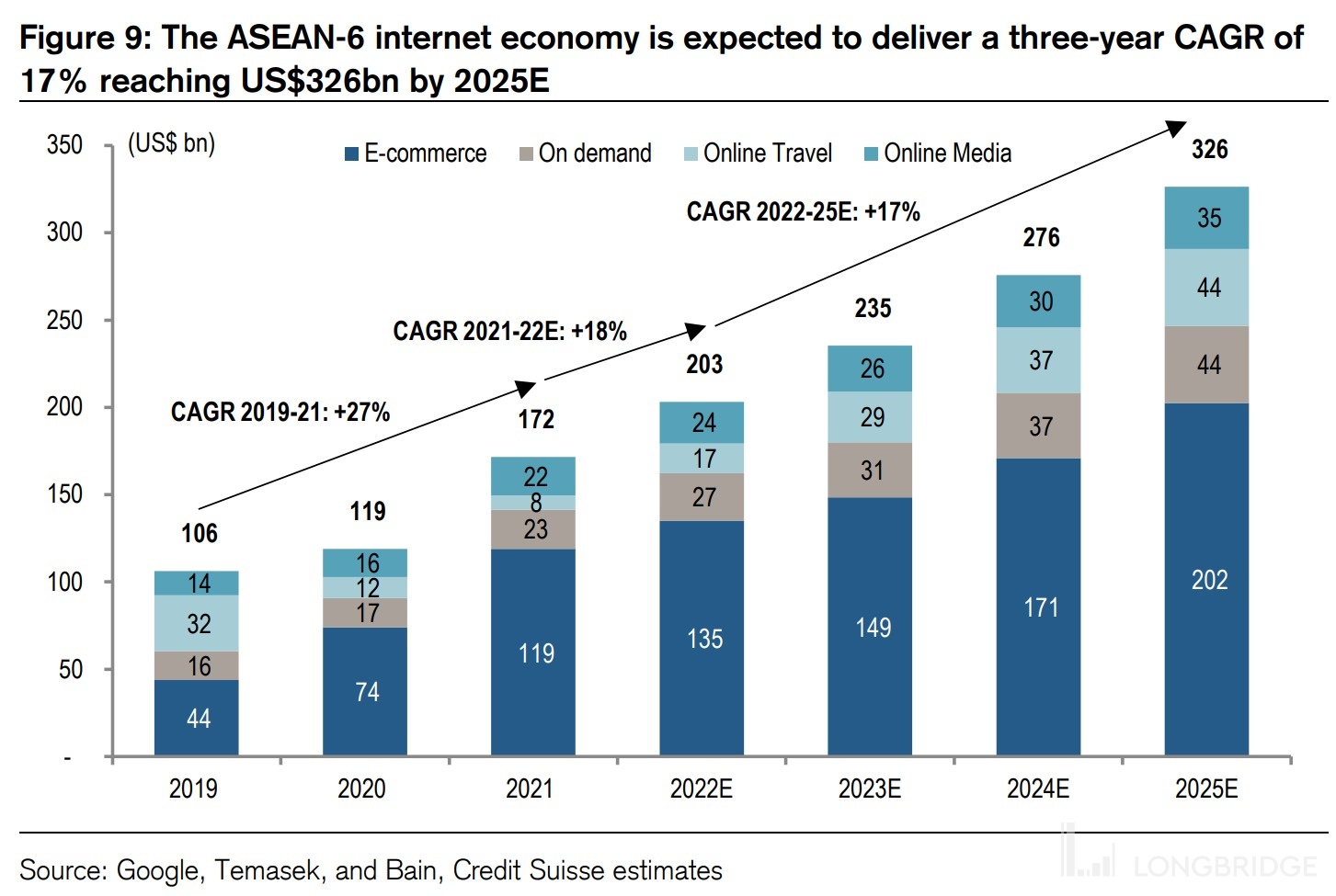
So, how is the e-commerce industry in the upstream of the express delivery sector performing in Southeast Asia? According to the Southeast Asia Online Economy Report jointly released by Google and Bain, the compound annual growth rate of the e-commerce market in Southeast Asia was 66% from 2015 to 2018, and the compound growth rate from 2019 to 2021 is still 27%, indicating that the e-commerce industry in Southeast Asia is still maintaining a relatively high growth rate.
However, due to the impact of the US dollar interest rate hike, rising energy costs, and the recovery of offline consumption, the growth rate of the e-commerce industry in Southeast Asia has also slowed down since 2022. But looking at the medium to long term, ignoring the fluctuations of the past 2-3 years, the potential growth rate of the Southeast Asian e-commerce market is likely to be higher than that of the domestic market. Therefore, the subsequent growth rate of the express delivery industry in Southeast Asia will also be relatively higher.
In China, J&T is like Pinduoduo, but in Southeast Asia, it is like SF Express.
Based on our previous analysis, we can see that J&T is the sixth player in the Chinese market, and there is still a considerable gap in key operational efficiency compared to other leading players. It has not yet achieved a balance between profits and losses and can only be considered as a challenger with an uncertain future.
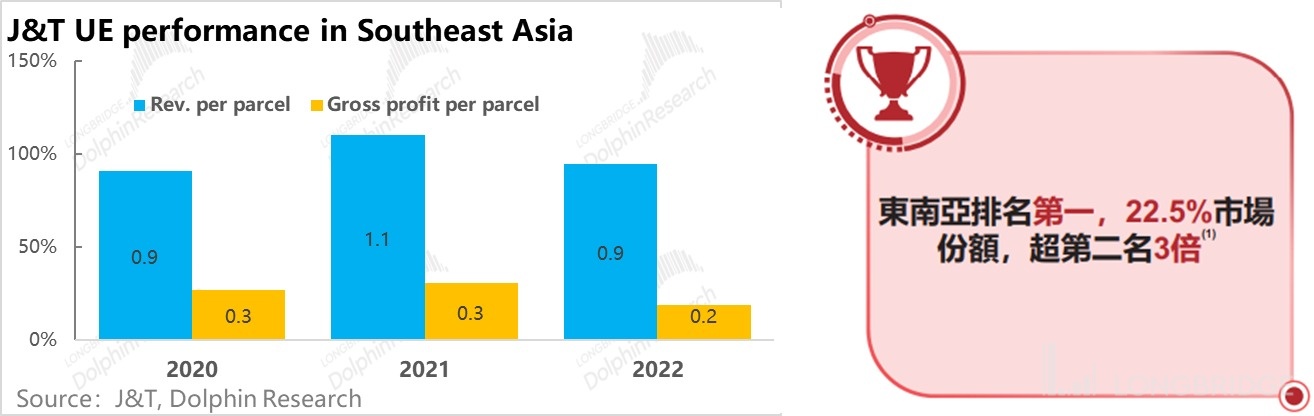
According to the prospectus, J&T has a market share of 22.5% in Southeast Asia, which is three times higher than the second-ranked player. It can be seen that J&T is the absolute industry leader in the express delivery market in Southeast Asia, and its position is even higher than that of ZTO Express and SF Express in the domestic market.
In terms of profitability, compared to the average revenue of $0.3 per order and negative gross profit per order in the domestic market, J&T's average revenue per order in Southeast Asia is close to $1, and the average gross profit per order is $0.2-$0.3. It can be seen that the profitability of J&T's business in Southeast Asia far exceeds that of its domestic business.
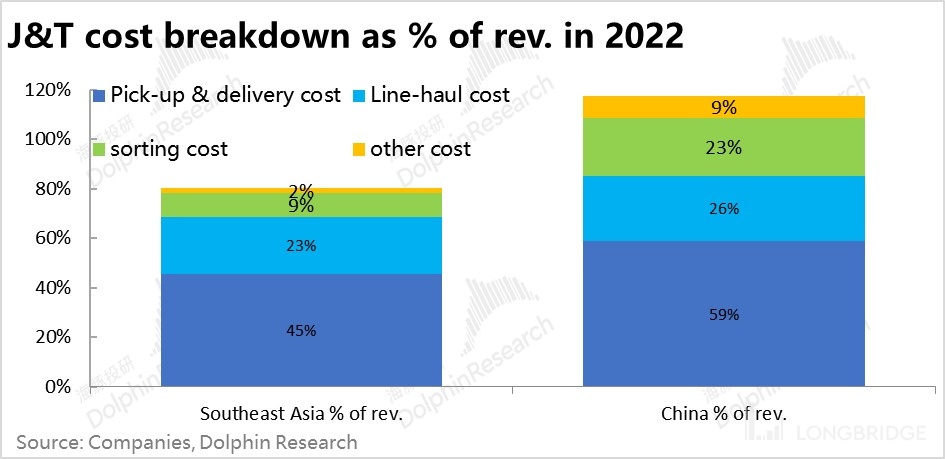
So why is there such a huge difference in profitability for the same J&T in two different markets? First of all, from the perspective of financial/operational data, the significantly higher average package price in both markets is a natural reason. However, from the perspective of relative operational efficiency (represented by the proportion of average transportation costs to average revenue), the cost items of J&T in Southeast Asia (delivery, sorting, trunk transportation, etc.) account for a lower proportion of revenue compared to the domestic market.And from the core business methods/philosophy of the company, what differences have led to the divergent performance of J&T in the two markets? Although Dolphin Research has no first-hand experience of J&T's delivery service in Southeast Asia, according to multiple channel surveys and feedback, J&T's operations in China are similar to Pinduoduo, advocating a rough and rugged style of "just enough" management, but when it first started in Southeast Asia, it was once regarded as the "SF Express of Southeast Asia", emphasizing service quality and meticulous management. Dolphin Research believes that this fundamentally opposite business philosophy is the root cause of the huge performance difference of J&T in the two markets.
According to market feedback, J&T has taken the following "unique" measures in the express delivery industry in Southeast Asia, which has made it the largest express delivery company in the region?
① Significantly improving delivery efficiency: Due to the numerous islands and underdeveloped transportation infrastructure in Southeast Asia, coupled with the low efficiency of many logistics and express delivery companies, even parcels are left unattended on rest days, resulting in high delivery costs and poor timeliness in the express delivery industry in Southeast Asia. It takes 2-3 days for express delivery between major cities, and even more than a week for non-major cities.
At the beginning of its business in Indonesia, J&T adopted a unique 24/7 uninterrupted operation mode. By reducing the impact of working mode, J&T has taken a significant lead in customer service and delivery efficiency compared to local express delivery companies. J&T even once launched the "compensation for late delivery" measure to improve delivery efficiency for its franchisees.
② More intensive stores & stricter management requirements: On the other hand, due to their own profit considerations, franchisees of local express delivery companies in Indonesia often rely on a single warehouse to cover the entire city, resulting in a delay of several days for local delivery after the parcels arrive at the destination. However, J&T has set up multiple distribution points under its city transit warehouse, reducing the delivery radius and increasing sales. It requires that "all packages arriving at the warehouse during business hours (8 am to 5 pm) must be dispatched on the same day, and packages arriving outside business hours must be delivered to the distribution point by 8 am the next day, and the distribution point must complete the delivery on the same day without any remaining packages."
It can be seen that in Southeast Asia, J&T relies on the same business philosophy as the leading express delivery companies in China (ZTO Express and SF Express), which is "fast delivery, good service, and strict management", as well as the "reducing impact" operating model of the Chinese express delivery industry, which has almost overwhelmed the original express delivery companies in Southeast Asia and become the number one in Southeast Asia.
Looking at it from a different perspective, can J&T defeat the leading players in the domestic express delivery industry, who have already achieved near-perfect operational efficiency, with its rough and rugged approach of "cheap and sufficient"? (The difference between the best ZTO Express and the worst STO Express may be no more than 95 points compared to 90 points). Dolphin Research believes the answer is unlikely.
Discussion on Valuation
In the previous sections, we discussed the different operating models of Rabbit Express in the domestic and Southeast Asian markets, explaining why Rabbit Express has different market positions and financial performance in these two regions.
Next, we will separately evaluate the valuation of Rabbit Express in these two markets, and then make an investment judgment on whether the current issuance price of HKD 12 and the market capitalization of approximately HKD 105.7 billion are reasonable. As for the cross-border business and emerging markets such as the Middle East, since the current revenue scale is only a few hundred million US dollars and the volume is small, and it is still in a huge loss state, it is difficult to judge the future revenue scale and profit inflection point. Therefore, we will not assign a valuation to this sector and will not impose a punitive valuation for losses.
1. Chinese Market
For the Chinese market, based on our analysis in the previous sections, the high-growth dividend period of Rabbit Express has basically passed. The latest data for the first half of 2023 also shows that the growth rate of Rabbit Express in China has declined to 15%, which verifies the fact that Rabbit Express's growth has slowed down rapidly. We believe that Rabbit Express's performance in China in the future will mainly depend on its progress in improving operational efficiency and reducing unit costs. However, at present, we believe that Rabbit Express still has a gap to reach the efficiency level of the top three express delivery companies, let alone gaining a competitive advantage.
In terms of industry competition, the growth trend of the e-commerce business is still weak. In addition to the top three express delivery companies, JD Logistics and Cainiao Logistics are also expanding their domestic express delivery business due to the pressure of independent operation. Even the weakest player, Shentong Express, has obtained investment from Cainiao. Therefore, it is highly likely that the domestic express delivery industry will maintain a high-intensity competition, and the vision of capacity clearance and industry profit recovery is unlikely to be realized within one or two years.
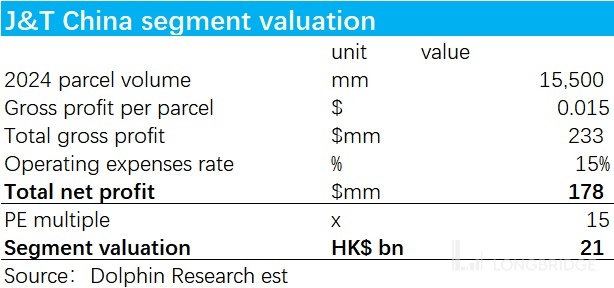
Therefore, our judgment on Rabbit Express in the future is as follows: It is already quite good for Rabbit Express to maintain a market share of 6% in the domestic market, and it is difficult to further increase its share. In terms of per capita profit, we are optimistic that Rabbit Express will reach the level of Shentong Express by 2024, and based on similar market positions and operational efficiency, we will assign Rabbit Express a PE multiple similar to Shentong Express in 2024. Based on these key assumptions, we estimate the valuation of Rabbit Express's express delivery business in China to be approximately HKD 21 billion.
2. Southeast Asian Market
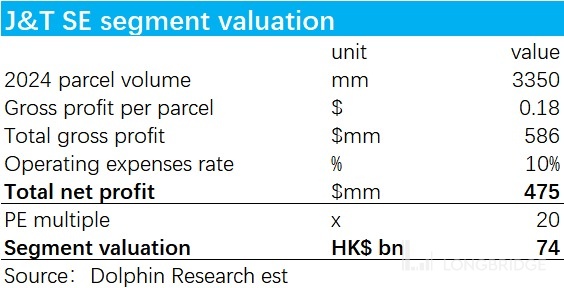
As for the Southeast Asian market, Dolphin Research believes that the industry will continue to grow at a higher rate than the domestic market in the future. In terms of competition landscape, as the stronghold of Rabbit Express, we have not yet seen any factors that can significantly change the local market share structure. Therefore, it is highly likely that Rabbit Express's performance will continue to grow steadily along the current trend. However, we also note that the average revenue and gross profit margin per delivery of Rabbit Express in the Southeast Asian market have shown a clear downward trend during the reporting period. Considering the significantly higher express delivery costs in Southeast Asia compared to the domestic market, as the e-commerce market continues to grow in scale, with the effects of economies of scale and the gradual development of transportation and logistics infrastructure, Dolphin Research predicts that the trend of declining average revenue per delivery may continue in the near future. In terms of valuation multiples, due to Rabbit Express's competitive advantage in Southeast Asia, we refer to the domestic industry leader, SF Express, and assign a PE multiple of approximately 20x.
3.Summary
Taking into account the valuation of the A-share market for express delivery companies, the overseas-listed ZTO Express has a PE multiple of less than 15x.
Based on the combined valuation of the two regions and the net cash owned by the company, we estimate that GTO's fair value is approximately HKD 96 billion, corresponding to HKD 10.9 per share. Therefore, Dolphin Research believes that the current issuance price of HKD 12 per share fully reflects GTO's visible profit level and may have given a certain valuation to its early-stage cross-border and new market businesses.
In terms of short-term valuation, the company's issuance price is not cost-effective. However, in terms of long-term potential and competitiveness, it is unlikely that GTO will continue to seize market share or achieve significantly higher average profits than its peers in the domestic market. The main potential lies in Southeast Asia and cross-border business.
Therefore, from a fundamental perspective, GTO is not a trend investment opportunity for long-term holding. However, the company's public offering of shares accounts for only about 3%+ of the total shares, with a small proportion of circulating shares. The stock price may experience significant fluctuations in the early stages of listing. For such short-term investment opportunities, Dolphin Research can only recommend seizing them.
Risk Disclosure and Statement: Dolphin Research Disclaimer and General Disclosure
The copyright of this article belongs to the original author/organization.
The views expressed herein are solely those of the author and do not reflect the stance of the platform. The content is intended for investment reference purposes only and shall not be considered as investment advice. Please contact us if you have any questions or suggestions regarding the content services provided by the platform.

